|
Interactive Generalized
Penetration Depth Computation for Rigid and Articulated
Models using Object Norm
Paper (PDF
6.7M)
Video (Download 20.7M)Source Codes (coming soon)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
[Abstract] We present a novel, real-time algorithm to accurately approximate the generalized penetration depth (PDg) between two overlapping rigid or articulated models. Given the high complexity of computing PDg, our algorithm approximates PDg based on iterative, constrained optimization on the contact space, defined by the overlapping objects. The main ingredient of our algorithm is a novel and general formulation of distance metric, the object norm, in a configuration space for articulated models, and a compact closed-form solution for it. Then, we perform constrained optimization, by linearizing the contact constraint, and minimizing the object norm under such a constraint. In practice, our algorithm can compute locally optimal PDg for rigid or articulated models consisting of tens of thousands of triangles in tens of milliseconds. We also suggest three applications using PDg computation: retraction-based motion planning, physically-based animation and data-driven grasping. |
|
Benchmarking Scenarios
Benchmarking
models with triangle counts. Rigid
Benchmarking Models with Triangle Count. CAD (2.4K), Spoon (1.34K), Dragon
(174K), Bunny (40K), Torusknot (3K), L-shape(20),
Cup (1K), Pawn (0.3K), Bumpy-Sphere (2.9K), Hammer (1.7K).
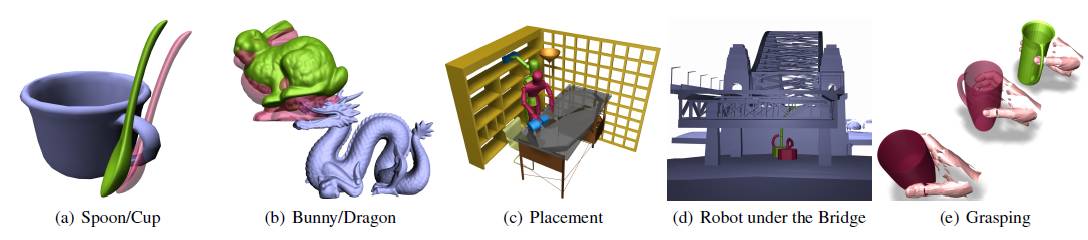
Interactive Generalized Penetration Depth (PDg) Computation. (a, b) As a result of PDg computation for rigid models, the red, colliding objects are rigidly transformed to the green ones, just in contact with obstacles. PDg computation for articulated models and application to motion planning (c, d)and grasping (e). Our algorithm can compute PDg for these challenging benchmarks at interactive rates. The models in (c), (d) and (e) were obtained fromthe GAMMA and KIT research groups, respectively, under permission.
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Performance for Articulated Models.
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
Performance in
|
|||||||||
Related Links
|
C2A: |
|
|
|
PQP: |
|
|
|
PolyDepth: |
|
|
|
Copyright 2014 Computer Graphics Laboratory |
|
Dept of Computer Science & Engineering |
|
Ewha Womans University, Seoul,
Korea |
|
Last update: Jan 6th, 2014 |


